08 Jun Foreign Body
Retained foreign bodies are very common injuries of the foot. In the body, over 50 percent of foreign body injuries occur in the foot. The most common retained foreign bodies of the foot include needles, glass, wood, metal, plastic, stone and shoe soles/socks (from a puncture wound). Due to the complications of retained foreign bodies, one should have them surgically removed.
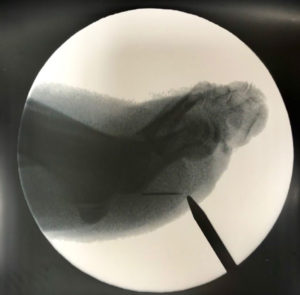
Your foot and ankle specialist will take x-rays in the office to determine the depth and location of the retained foreign body. In the operating room your podiatrist will use a C-Arm (x-rays) to triangulate and locate the retained foreign body which will aid with incision placement and minimize trauma to the surrounding tissues.
Retained foreign bodies can cause many types of complications in the foot and they should be removed. Potential complications of retained foreign bodies in the foot include migration, infection, joint stiffness (if within a joint), granuloma formation and chronic pain. Infection is the most common complication of a retained foreign body and wood foreign bodies carry the highest risk of infection and inflammation.
If you’ve stepped on an object or think that you have, visit your foot and ankle surgeon to be evaluated.