19 Mar Bunions
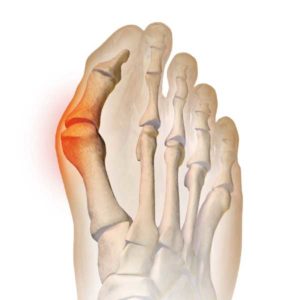
The classic bunion is a bump on the side of the great toe joint. This bump represents an actual deviation of the 1st metatarsal. In addition, there is also deviation of the great toe toward the second toe. In severe cases, the great toe can either lie above or below the second toe.
What causes bunions? This question is often answered by blaming shoes. But in fact, shoes only play a small role in developing bunions. Yes, shoes, especially high heels cause abnormal squeezing of your forefoot. This in turn to help promote a bunion. But if everyone who wore high heels shoes had a bunion, there would be a lot more then the 15% prevalence we see in the general population. As you can see from the flow chart, genetics plays the major role in development of bunion deformities.
Genetics determines the way your foot functions. Are you flatfooted? Are your joints flexible or stiff? Do you have a high arch? Do you have tight muscles? These traits are determined by your genetic code. These characteristics then govern how your bones and joints move when you walk. As an example, if your joints are very flexible, this can cause an abnormal amount of instability in your forefoot when you walk. Over time, this abnormal motion will cause the a bunion to develop by allowing your first metatarsal to “drift” towards the mid-line of your body.
The fundamental driving force behind developing bunions as a result of faulty foot mechanics is genetics. Issues such as loose ligaments and flat feet, are inherited. The traits then act as the foundation for abnormal foot mechanics and lead to formation of bunions.
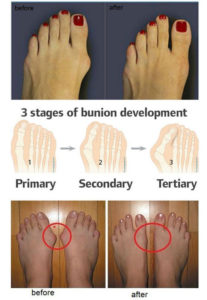
Symptoms
The most common symptoms associated with this condition are pain on the side of the foot just behind the great toe. A red painful bump is usually present. Pain is usually brought on with walking or sports. Shoes don’t cause bunions but will typically aggravate them. Stiff leather shoes or shoes with a tapered toe box are the prime offenders. This is why bunion pain is most common in women whose shoes have a pointed toe box. The bunion site will often be slightly swollen and red from the constant rubbing and irritation of a shoe. Occasionally, corns can develop between the 1st and 2nd toe from the pressure the toes rubbing against each other.

